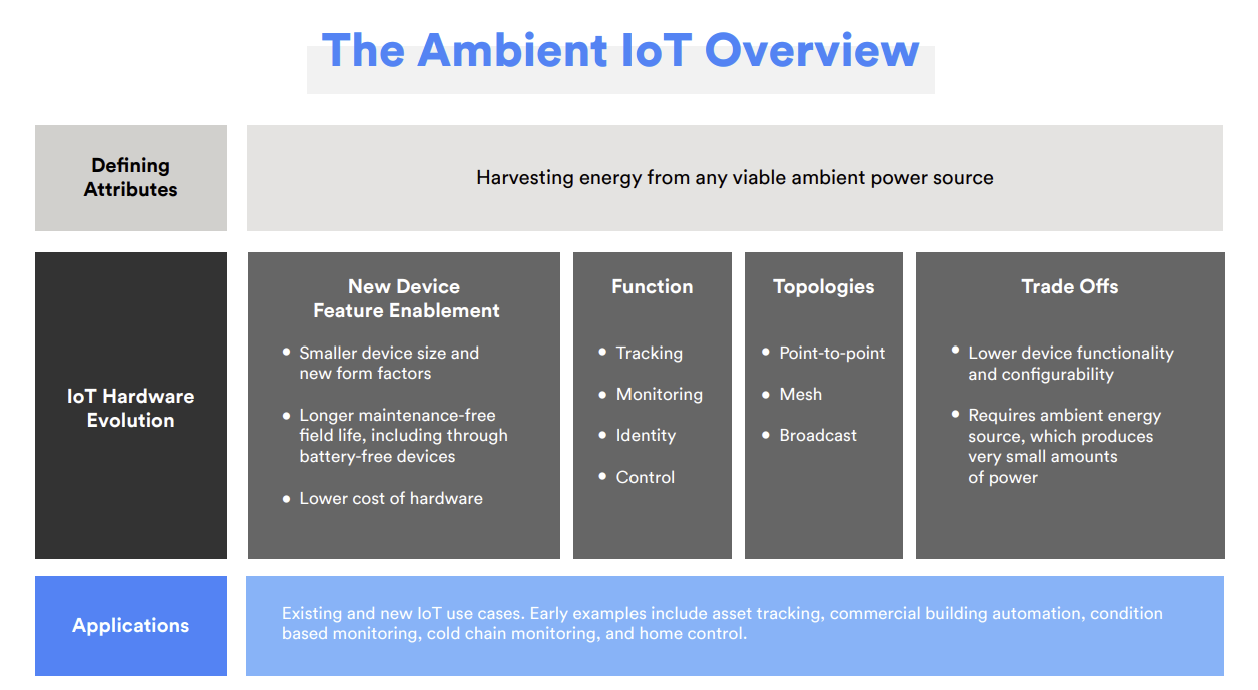
The next stage of evolution for IoT devices, the Ambient IoT refers to a new class of connected devices primarily powered by harvesting energy from any viable ambient source. These devices were built from innovative form factor designs and support low-maintenance or maintenance-free operation.
Recently, the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) commissioned ABI Research – a global leader in analyzing, tracking, and forecasting the transformation of the smart device and IoT markets – to establish guidelines for understanding the Ambient IoT and evaluate the role of Bluetooth® technology in addressing Ambient IoT use cases.
Defining the Ambient IoT
The Ambient Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a new class of IoT devices primarily powered by harvesting ambient energy from radio waves, light, motion, heat, or any other viable ambient energy source.
The Ambient IoT is an extension of the existing IoT. Ambient IoT devices carry out many of the same functions as IoT devices and target many of the same use cases but require additional design choices to meet solution demands. By relying on energy harvested from ambient sources, the Ambient IoT makes it possible to develop lower-cost, smaller, and maintenance-free devices, allowing the IoT to become more scalable in existing use cases and in use cases still to be developed. For instance, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), depending on the use case and environment, may choose to make self-sustaining devices, assisted by batteries or capacitors, by powering them with ambient energy. Alternatively, they may decide to go a step further and create battery-free devices with more flexible form factors and a lower bill-of-materials (BOM) cost.
Harvesting energy from ambient sources generates only minimal amounts of power. This creates the inherent requirement for Ambient IoT devices to be less complex and more power efficient. This can be addressed by optimizing the radio protocol and adding features, such as embedded intelligence, to make devices wake up and collect or transmit data less frequently.
The market opportunity for this new class of IoT devices is extensive. Ambient energy harvesting devices today are primarily centered on short-range wireless connectivity, particularly Bluetooth® technology. Looking ahead, there is widespread interest in comprehending and aiding the development of this emerging category of devices. The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), overseeing cellular standards, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), responsible for Wi-Fi and network standards, and the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), responsible for Bluetooth® technology standards, are engaged in consultations with IoT developers. They aim to explore ways to facilitate the growth of the Ambient IoT. This collaborative effort underscores the cross-industry support and commitment to defining and supporting the Ambient IoT.
![]()
NEW MARKET RESEARCH
The Ambient IoT – The Emergence of a New Class of Bluetooth® IoT Devices
This report defines the Ambient IoT, outlines targeted use cases, and highlights the next steps needed to capitalize on the Ambient IoT opportunity. It also explains the central role of Bluetooth® technology in addressing Ambient IoT use cases, characterized by its low power consumption, low cost, flexibility, interoperability, and scalability.
Why We Need the Ambient IoT
The Ambient IoT addresses the needs of technology adopters by expanding the IoT in directions that are impossible to achieve with traditional devices. Key ways in which the Ambient IoT will contribute to the expansion of the IoT include:
- Maintenance-Free Devices: Maintaining IoT installations in the field can be a time-consuming and costly exercise, adding a layer of complexity to operations that the IoT is designed to make more efficient. Ambient IoT devices can be deployed in autonomous settings without maintaining a continuous power supply or replacing batteries. Low-maintenance or maintenance-free devices can change paradigms for return-on-investment (ROI) calculations by guaranteeing the longevity of deployments.
- Low Complexity and Cost: The Ambient IoT continues the trend toward lower cost and simpler devices. By relying primarily on ambient energy sources, the Ambient IoT will encourage the design of devices that communicate less frequently and are designed to fulfill specific functions, driving an evolution away from highly configurable devices streaming real-time data.
- Sustainable Devices: Replacing batteries, or throwing away battery-powered devices, is a challenge to the sustainable growth of the IoT. According to the European Union (EU)-funded project, EnABLES, a forecasted 78 million batteries will be discarded daily by 2025, assuming an average two-year battery life for IoT devices. Harvesting energy from ambient sources can create longer-lasting and self-sustaining Ambient IoT devices, whether by extending the life of battery- or capacitor-powered devices indefinitely or by removing batteries from devices entirely.
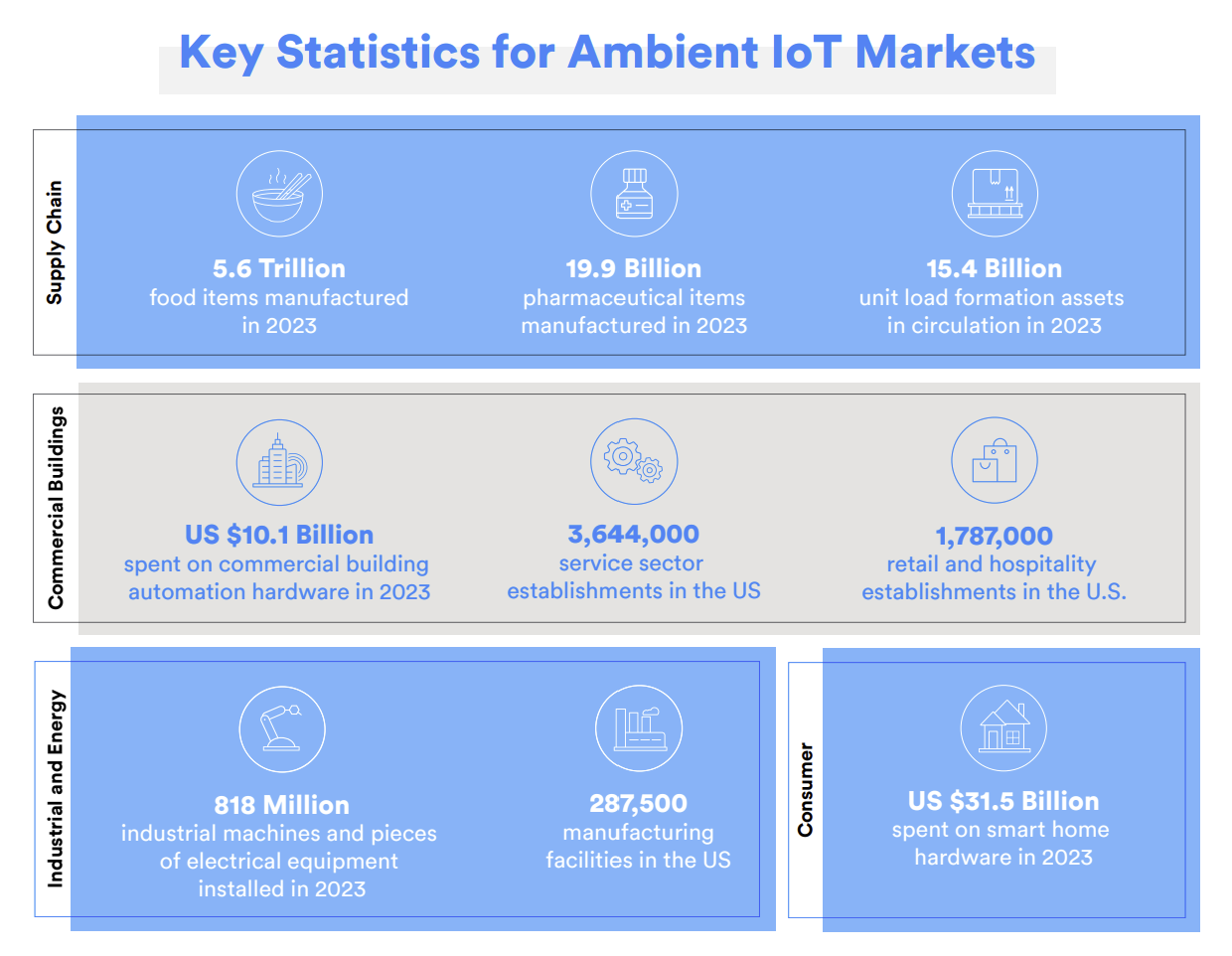
As technologies supporting the Ambient IoT devices mature, and support ambient energy harvesting, use cases outside of goods tracking and monitoring will multiply. Use cases span many vertical markets. In industrial markets, potential use cases involve sensor-based monitoring of machine conditions, equipment status, environmental conditions, or electronic labeling. In commercial markets, use cases include building automation and control, air quality monitoring, and electronic shelf labels (ESLs) in retail markets. In consumer markets, use cases include personal tracking or various home automation systems. As these use cases demonstrate, the Ambient IoT will initially serve existing IoT applications with a new device class. As the market expands, it will help create entirely new application areas. The image below highlights some key statistics for markets that the Ambient IoT can target.
Evolving the IoT
The emergence of Ambient IoT devices represents a significant leap in the evolution of IoT devices, offering a promising future for the IoT ecosystem. By relying on ambient energy sources, the Ambient IoT enables the development of lower-cost, smaller form factor, and maintenance-free devices, thus opening new possibilities for IoT applications across various industries.
The market potential is extensive with early adoption focused on short-range wireless connectivity, particularly Bluetooth® Low Energy (LE) technology. Bluetooth LE will play a central role in the evolution of the Ambient IoT. From a technology perspective, it is a leading, very low-power protocol that supports a wide range of network topologies and is available on many low-cost ICs. From an ecosystem perspective, Bluetooth® LE is an open, standard-backed technology that promises long-term support and feature evolution. Consequently, it has built a large developer base and a ubiquitous installed base of dedicated or multi-use infrastructure, facilitating further solutions built with the technology.
To learn more, read the full report: The Ambient IoT – The Emergence of a New Class of Bluetooth IoT Devices. This report helps define the Ambient IoT and outlines the role Bluetooth technology plays in its evolution.
![]()
NEW MARKET RESEARCH
The Ambient IoT – The Emergence of a New Class of Bluetooth® IoT Devices
This report defines the Ambient IoT, outlines targeted use cases, and highlights the next steps needed to capitalize on the Ambient IoT opportunity. It also explains the central role of Bluetooth® technology in addressing Ambient IoT use cases, characterized by its low power consumption, low cost, flexibility, interoperability, and scalability.
アンビエントIoTは、IoTデバイスの進化における新たな段階に位置付けられます。アンビエントIoTとは、周囲に存在する環境エネルギー源からエネルギーを取り込んで主な電力源とすることができる、新たなクラスのコネクテッドデバイスです。アンビエントIoTは、革新的なフォームファクター設計と、メンテナンスの必要性が少ない、またはメンテナンスを全く必要としないデバイスの実現を可能にします。
先日Bluetooth SIG(Special Interest Group)は、アンビエントIoTを理解し、アンビエントIoTのユースケースにおけるBluetooth®技術の役割を精査するための指針を確立するため、ABI Researchに調査を依頼しました。同社はスマートデバイスおよびIoT市場の変革に関する分析・追跡・予測分野の世界的トップ企業です。
アンビエントIoTの定義
アンビエントIoT(モノのインターネット)とは、電波、光、運動、熱など、周囲に存在する環境エネルギー源からエネルギーを取り込み主な電力源とする、新しいクラスのIoTデバイスです。
アンビエントIoTは既存のIoTの延長線上にあります。そのためIoTデバイスと同様の機能を多く備え、同様のユースケースの多くが対象となりますが、ソリューションに必要とされる要件を満たすため、設計面での追加事項が生じます。アンビエントIoTは、周囲のエネルギー源から取り込んだ環境発電エネルギーを使用するため、より低コストで小型、かつメンテナンスフリーなデバイスの開発を可能にし、既存のユースケースや開発中のユースケースで、よりスケーラブルなIoTを実現します。例えばOEMは、ユースケースや環境に応じてバッテリーやコンデンサーで補助的に電力供給しつつ、周囲のエネルギーから電力を供給する自立型デバイスを設計することも可能です。また、さらに一歩進んで、より柔軟なフォームファクターを使い、部品表(BOM)コストの低い、バッテリーフリーのデバイスを開発することも考えられます。
周囲のエネルギー源からの環境発電によって得られる電力はわずかです。このため、アンビエントIoTデバイスでは、複雑さを抑え、消費電力の効率に優れていることが固有の要件となります。この要件には、無線プロトコルを最適化し、組み込みインテリジェンスなどの機能を追加して、デバイスのウェイクアップやデータの収集・送信の頻度を減らすことで対処できます。

アンビエントIoTデバイスの市場機会は広範囲に及びます。現在、環境発電デバイスは、主に近距離無線接続、特にBluetooth®技術が中心となっています。そして、この新たなカテゴリーのデバイスを理解し、その開発を支援することに広い関心が寄せられています。携帯電話の規格を統括する3GPP(3rd Generation Partnership Project)、Wi-Fiやネットワーク規格を統括するIEEE(Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)、Bluetooth®技術規格を統括するBluetooth SIG(Special Interest Group)の3団体は、IoT開発企業との協議を続けています。これらの関係者が目的としているのは、アンビエントIoTの成長を推進する方法の模索です。この協力的な取り組みは、アンビエントIoTの定義とサポートに対する、業界を超えた支援とコミットメントを体現しています。
アンビエントIoTが必要とされる理由
アンビエントIoTは、従来のデバイスでは実現できない方向へのIoTの拡張を可能にし、技術を適用する企業や開発者のニーズに応えます。アンビエントIoTは、主に次のような形でIoTの拡張に貢献します。
- メンテナンスフリーのデバイス:現場におけるIoT設備のメンテナンスには時間とコストがかかり、効率化をもたらすはずのIoTに、複雑な手順を追加します。アンビエントIoTデバイスは、継続的な電力供給やバッテリー交換を必要とせず、自律的な設定での実装が可能です。デバイスのメンテナンス頻度が少ない、またはメンテナンスフリーであることにより、長期間の運用が保証され、投資収益率(ROI)計算のパラダイムが変わります。
- 複雑さとコストを抑える:アンビエントIoTは、「より低コストでよりシンプルなデバイス」を求める現在のトレンドに合致します。主に環境エネルギー源を利用することにより、アンビエントIoTは、より通信頻度が低く特定の機能を満たすためのデバイスの設計を促進します。これにより、リアルタイムデータのストリーミングを伴う、高度な設定が可能なデバイスから距離を置く形での進化が促されます。
- 持続可能なデバイス:IoTにおける持続的な成長の観点から、現在、バッテリーの交換や、バッテリー駆動機器の廃棄が課題となっています。欧州連合(EU)が資金を提供するプロジェクト「ENABLES」は、IoTデバイスのバッテリー平均寿命を2年と想定し、2025年までに毎日7800万個のバッテリーが廃棄されると予測しています。周囲のエネルギー源からの環境発電は、より長寿命で、それ自体が持続性を持つアンビエントIoTを生み出します。そうしたデバイスは、バッテリー駆動またはコンデンサ駆動のデバイスの寿命を限りなく延ばすことにより、あるいはデバイスからバッテリーを完全に取り除く形で実現されます。
アンビエントIoTデバイスをサポートする技術が成熟し、能力が上がるにつれて、商品の追跡・監視以外のユースケースの増加が見込まれます。ユースケースはさまざまな垂直市場に及びます。産業市場では、可能性のあるユースケースとして、機械・機器の状態、環境条件、電子ラベルのセンサーベースでの監視などが挙げられます。商業市場ではビルオートメーション・制御、空気の質の監視、小売市場における電子棚札(ESL)といったユースケースが、また消費者市場では、個人の追跡やさまざまなホームオートメーションシステムなどのユースケースが考えられます。これらのユースケースが示すように、アンビエントIoTは新たなデバイスクラスを用いながら、まずは既存のIoTのユースケースに用いられます。そして市場の拡大に伴い、まったく新しい用途分野を切り開いていくことが見込まれます。下図は、アンビエントIoTの対象になり得る市場に関する主要な統計を示しています。

IoTの進化
アンビエントIoTデバイスの登場はIoTデバイスにとって飛躍的な進化であり、IoTエコシステムの豊かな将来性を約束しています。環境エネルギーを使用することにより、アンビエントIoTはより低コストで小型、メンテナンスフリーのデバイスの開発を可能にし、さまざまな業界にまたがるIoTアプリケーションの新たな可能性の扉を開きます。
アンビエントIoT市場のポテンシャルは大きく、特にBluetooth® LE技術をはじめとする短距離無線接続では早期から採用が始まっており、市場は拡大を続けています。Bluetooth LEは、アンビエントIoTの進化において中心的な役割を果たします。Bluetooth® LEは、技術面では最先端の超低消費電力プロトコルであり、幅広いネットワークトポロジーに対応し、多くの低コストICで利用できます。また、エコシステム面では、オープンかつ標準によって支えられた技術として、長期的なサポートと機能の進化が約束されています。そのため大規模な開発者ベースが存在し、専用あるいは複数用途のインフラストラクチャのいずれにおいてもインストール済みのデバイスが遍在しており、この技術を用いたソリューションの構築を強力に後押しします。
詳しくは、「アンビエントIoT:Bluetooth®︎ IoTデバイスに新たなクラスが登場」のレポート本編をご覧ください。本レポートではアンビエントIoTがどのようなものであるかを解説し、その進化の中でBluetooth技術が果たす役割をまとめています。












