Wireless Connectivity Options for IoT Applications – Commercial Lighting
Industry 4.0 is no longer a thing of the future. The term describes the fourth revolution that has occurred in manufacturing and refers to the enhancement of smart and autonomous systems fueled by data and machine learning. Lighting systems are seen to play an important role as the foundation for this revolution.
In the past few years, the commercial lighting industry has gone through some dramatic changes. Commercial lighting solutions have evolved into much more advanced and sophisticated systems. The two main motivating reasons behind the adoption of more advanced lighting controls are:
- Significant reduction in energy costs
- Significant enhancement of occupant experiences
Here are some of the ways in which these systems have evolved:
- Going wireless instead of traditional wired configurations. This move is motivated by significantly lower costs of installation and ongoing maintenance, especially in retrofit solutions.
- Automating many of the functionalities that have traditionally been manual by nature. This move is primarily motivated by lower costs.
- Connectivity to the cloud for intelligence and decision making.
- Smart luminaires (which refers to a complete electric light unit) have expanded beyond the standard on/off and dimming functionality. They can now help provide performance monitoring, diagnostics metrics, and power efficiency.
- The luminaire has also evolved to include a plethora of sensors. Luminaires are becoming the nervous system of the building which can enable better operation of other building systems, including HVAC. Examples of sensors include occupancy sensors, photosensors, temperature sensors, humidity sensors, etc.
What Is Commercial Lighting and Why Is It Deployed?
A commercial lighting system refers to the lighting systems that are deployed in offices, stores, institutions, hospitals, industrial spaces, and factories. These systems tend to have a higher initial cost, longer lifespan, better durability, and higher maintenance and service costs when compared to residential lighting systems.
The main reasons commercial lighting systems are deployed include maximizing energy savings, satisfy building codes, and ensuring a comfortable occupant experience. It typically consists of the following components:
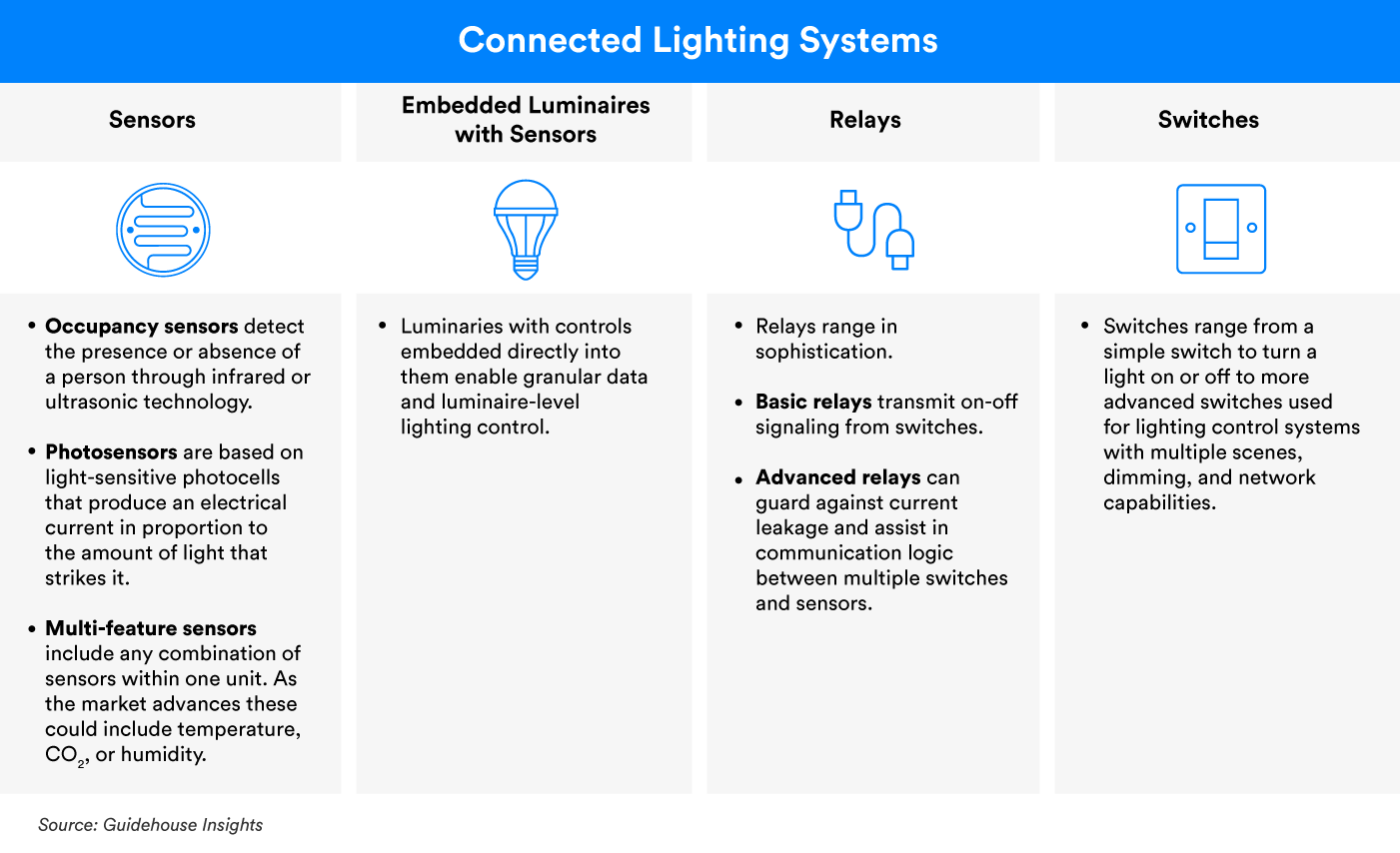
- Sensors: Occupancy sensors, photosensors, and other multi-feature environmental sensors such as temperature, humidity, CO2, etc.
- Luminaires: Refers to the light units themselves and all components directly associated with the distribution, positioning, and protection of the light unit
- Switches: Devices that control the light units, directly triggering functionality such as on/off and dimming capability
- Relays: Relays are sometimes used to either simply transmit control commands from switches or achieve more advanced intelligent functionality that involves logic and decision making before retransmitting the commands
Here’s a table (source: Guidehouse Insights) showing the different components of a connected lighting system:
Some of the benefits of deploying commercial lighting systems include:
- Increased environmental awareness and the potential to reduce power consumption via different sensors such as occupancy, photosensors, temperature, humidity, air quality, and more
- Higher efficiency and cost reduction when it comes to installation, deployment, commissioning, and maintenance
- Automation leading to more control and access to valuable, more granular data for advanced analytics
- Space utilization and optimization
- Infrastructure for other applications such as wayfinding and asset tracking within a facility
While the move to connected and smarter commercial lighting systems may seem like a straightforward choice for most facility owners and managers, it does face a set of challenges, some of which are:
- Lack of standardization in the industry
- Lack of awareness
- Poor reliability in some systems
- Security and privacy concerns
The move to wireless connectivity for commercial lighting systems promises a lot in terms of benefits and ROI (return on investment), but it needs to be able to accommodate retrofitting existing systems in order to deliver on these promises. The recent collaboration between wireless standards organization such as the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) and the DALI Alliance (DiiA) strives to combine the best IoT luminaire standard (DALI/D4i) with the best wireless lighting control standards. The DALI Alliance (DiiA) defines an open digital standard alternative to proprietary protocols for wired lighting systems which has become increasingly popular in the commercial lighting industry, especially in the European region.
Critical Attributes for Wireless Technologies Utilized in Connected Commercial Lighting
There are a few key attributes that need to be considered in wireless technologies utilized for commercial connected lighting applications. These are:
- Scalability & Performance
- Reliability
- Privacy & Security
- Cost
The priority given to each of these attributes in a specific application heavily depends on the facility and the desired functionality of the commercial lighting system being deployed. Let’s define each of these attributes within the context of connected commercial lighting:
Scalability & Performance
The scalability of a wireless network refers to its ability to grow (in the number of nodes) to adapt for future growth while having a limited impact on the performance of the network. Performance goes hand in hand with scalability. There’s no point in a network being able to scale while significantly decreasing its performance.
Performance of a wireless network refers to the measure of service quality of the network. In the context of commercial lighting, some of the most important performance measurements include latency, throughput, and signal error rate.
Reliability
Reliability refers to the ability to get a message from A to B within the time needed. The reliability of the wireless networks in commercial lighting applications is extremely important. Having sensor data points transmitted over a network that is not reliable could cause more harm than good. This is especially true for applications that are time sensitive.
Wireless networks employ various techniques to increase reliability. Some of these are at the protocol level, while others are at design and implementation.
The most common ones are:
- Data retransmissions in case of errors which relies on tracking the sequencing of data packets being transmitted and received
- Error detection and correction (e.g. data redundancy, forward error correction techniques, etc.)
- Increasing transmit power at the transmitter
- Increasing receiver sensitivity
- Multiple antennas at the receiver
- Frequency hopping to avoid noisy channels
Not all wireless network technologies are created equal, and some focus on reliability and robustness more than others. So, be sure to consider this parameter carefully when choosing a wireless network technology and really understand what mechanisms are utilized to achieve the level of reliability needed for your system.
Privacy & Security
Both privacy and security are major concerns when it comes to any wirelessly connected system. With the dramatically increasing amount of data collected in commercial lighting applications, protecting users’ privacy is becoming even more critical.
From a security perspective, wireless systems are much more vulnerable to attacks compared to wired systems. This needs to be taken into account when choosing a wireless technology to make sure the system is protected against cybercriminal attacks. Not all wireless technologies are created equal when it comes to security and privacy protection, so it’s important to evaluate how the chosen technologies achieve the level of protection appropriate for the application under consideration.
Cost
Two types of costs are involved with a commercial lighting system:
- Initial, one-time costs (hardware, deployment, installation, commissioning, and software)
- Recurring costs (maintenance, condition monitoring, and software)
It’s important to consider both types when selecting a wireless technology for your commercial lighting system.
Comparison of Wireless Technologies Most Suitable for Commercial Lighting
Based on the attributes mentioned above – scalability and performance, reliability, interoperability, privacy and security, and cost – here are the most suitable wireless technologies for the application of commercial lighting:
- Bluetooth® Mesh
- Zigbee
- Thread
Now, let’s compare the most common technologies in terms of the key attributes we listed.
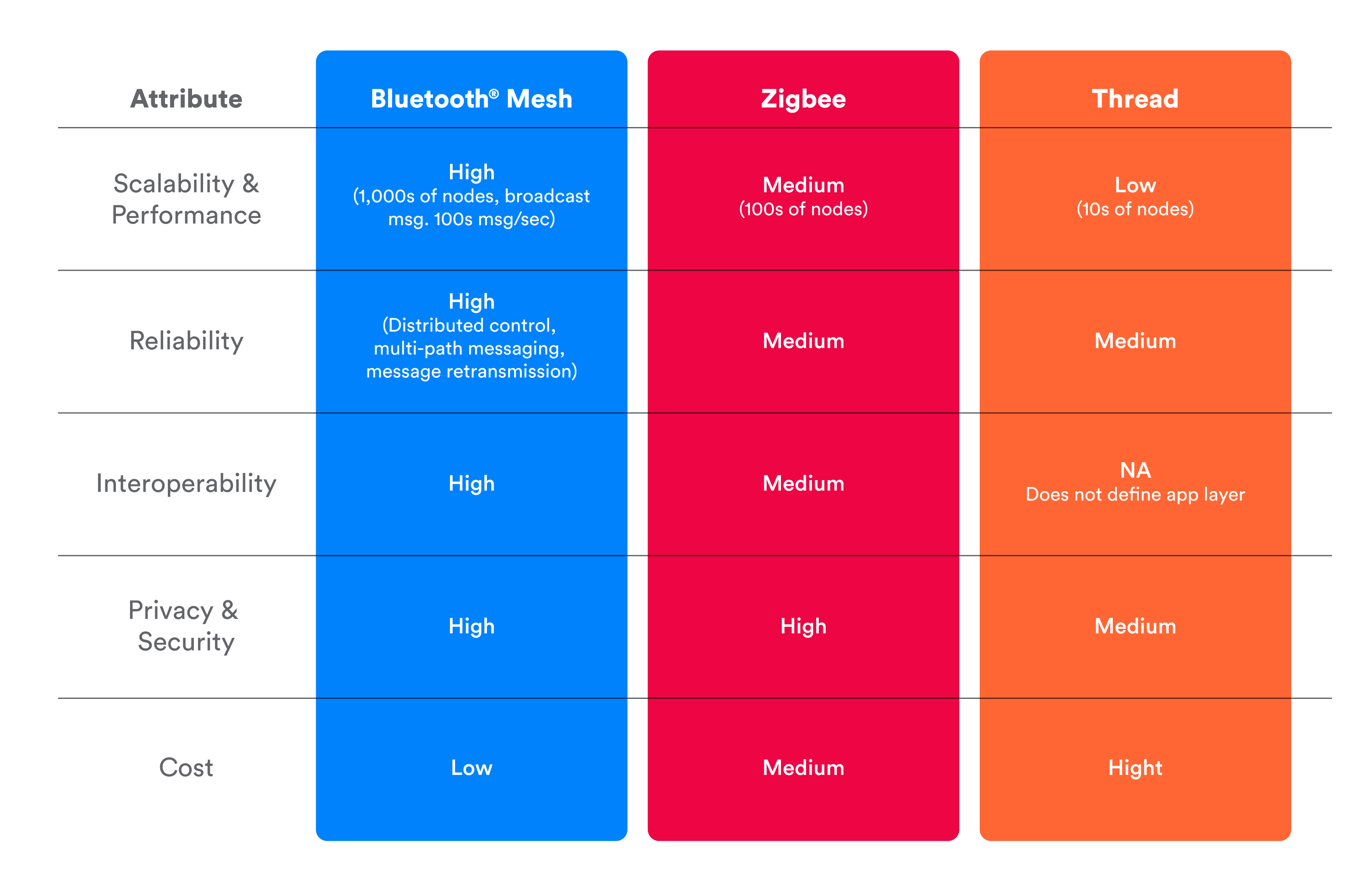
It’s important to keep in mind that some technologies are tailored more towards residential installations, and they would not necessarily be appropriate for commercial deployments.
Bluetooth® Mesh was designed from the ground up to address the needs of the commercial lighting space. The key fundamental characteristics that differentiate Bluetooth Mesh from other technologies are:
- Revolutionary distributed control architecture
- Revolutionary publish/subscribe message addressing
- Revolutionary managed flood message relay
These characteristics allow Bluetooth Mesh to handle common, large-scale industrial deployments in a more reliable and robust manner than other technologies.