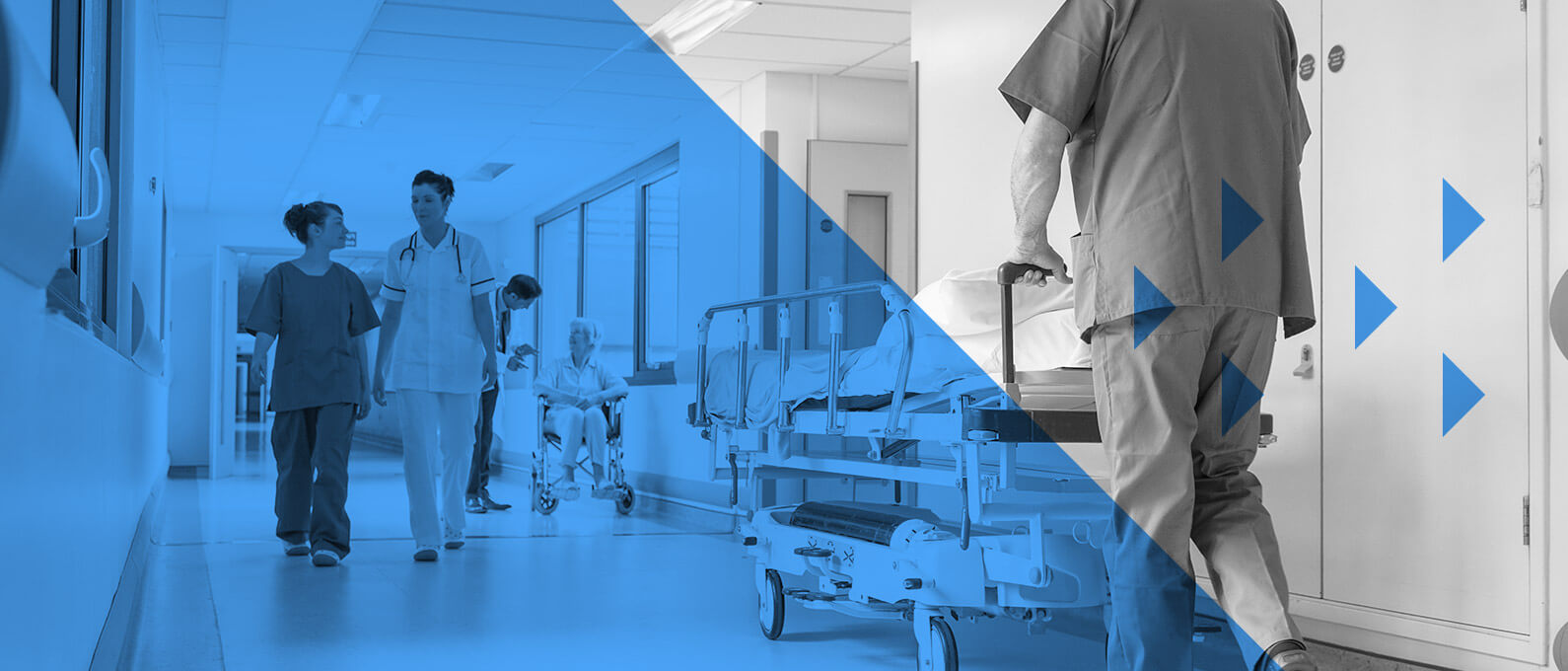
In recent years, Bluetooth® innovations have seen wider deployment across commercial spaces, including retail, hospitality, tourism, and medical. Now — thanks to the technology’s global proliferation, method of signal transmission, low power consumption, and capability to create large-scale device networks — Bluetooth technology is in a prime position to further enhance the healthcare experience for patients and staff.
Connectivity at Every Level
From fitness trackers and smartwatches to glucose monitors and pulse oximeters, Bluetooth enabled wearables have taken over the connected device market. New waves of wearable innovations are creating greater demands for monitoring devices that can support medical diagnosis and care. As such, Bluetooth® technology is increasingly replacing wired equivalents in recovery suites, operating rooms, and ICUs.
New expansions of the technology significantly enhance security, increase signal range, and strengthen asset tracking and wayfinding capabilities, widening the use cases for Bluetooth devices in healthcare facilities. Using Bluetooth technology, patients and visitors can easily navigate through a large hospital or medical campus while healthcare staff can quickly locate hospital assets like essential medical equipment and patients in need of urgent care.
Frequency Hopping
Concerns about adding radio-frequency technology to an environment already saturated with wireless signals can cause healthcare facilities to take pause. Having too many devices transmitting on highly used channels can create radio interference and distortion. But Bluetooth® technology uses adaptive frequency hopping (AFH) to minimize its impact in environments laden with wireless signals.
Through AFH, a Bluetooth device can see which channels are in use and avoid those channels in the hop sequence. This reduces radio impedance and allows Bluetooth packets to transmit through the toughest interference sources, making it an ideal add-on to any wireless infrastructure.
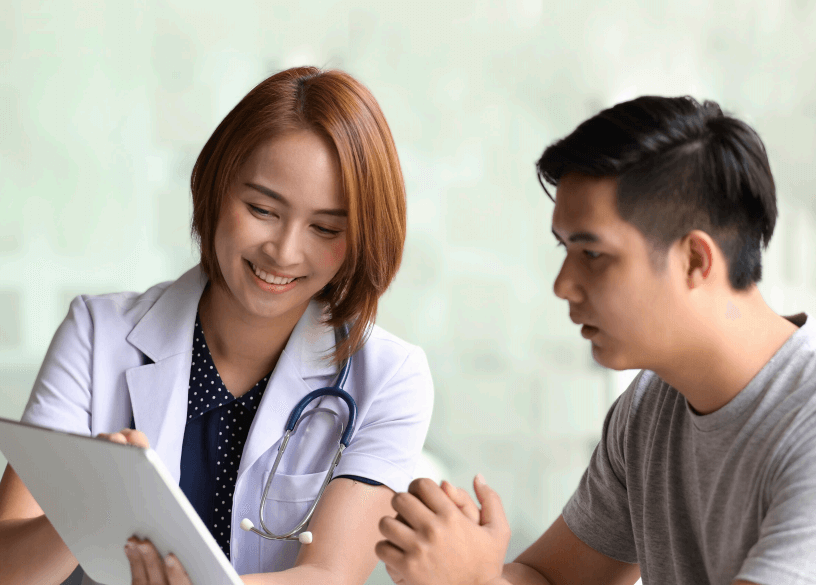

Low Energy Consumption
Since the adoption of Bluetooth® Low Energy (LE) in 2010, Bluetooth technology has supported optimized energy consumption on battery-powered devices that can transfer small amounts of data to local user interfaces like tablets and smartphones.
Healthcare spaces now employ a wide range of medical devices — such as blood glucose monitors, asthma inhalers, and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICD) — that use this technology to improve patient condition monitoring and care. Thanks to the power efficiency of Bluetooth LE, these devices can operate for years on small, coin-cell batteries. The lower-power properties of Bluetooth LE also support compliance requirements for environmental sensors and patient room monitoring.
Large-Scale Device Networking
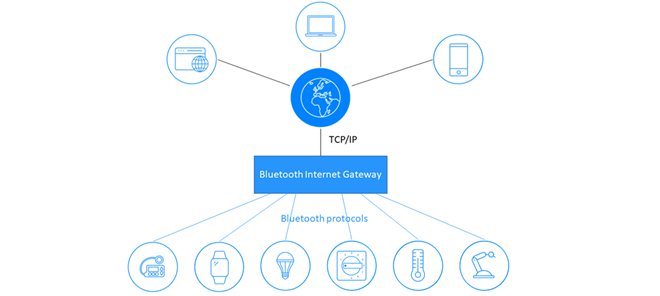
As the demand for comprehensive, secure wireless device networks continues to grow across commercial and industrial spaces, healthcare environments stand to benefit from the increased security, reliability, and scalability these facility-wide networks provide.
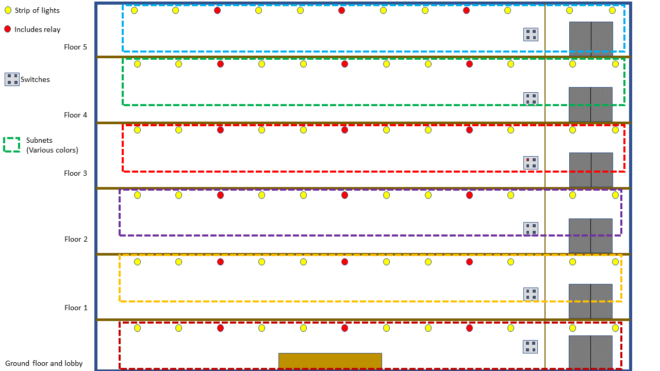
Bluetooth® Mesh enables the creation of large-scale device networks and is ideally suited for control, monitoring, and automation systems that require tens, hundreds, or thousands of devices to reliably and securely communicate with one another. A Bluetooth Mesh network can help healthcare facilities combat cost pressures, provide better patient care, and improve operational efficiencies by using Bluetooth technology to monitor patients and advance emergency services.
Download this white paper on Connectivity Choices for your Medical Device and IoMT Application and see how the latest wireless innovations are being used to support a wide range of healthcare applications.
![]()
FEATURED INFOGRAPHIC
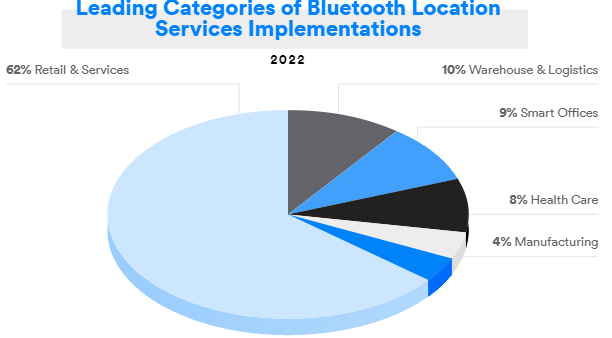
Bluetooth Location Services
See 8 use cases for enhancing building efficiencies and creating a better visitor experience, discover new data that supports the latest trends and forecasts, and find out what’s driving the rapid adoption of location services solutions.

![Forbes Predictions article 72 dpi 1300 x 680 px 768x402[1]](https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Forbes-Predictions-article-72-dpi-1300-x-680-px-768x4021-1-660x345.png)







![shutterstock 1653733096[1]](https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/shutterstock_16537330961-660x372.jpg)