Revision: v1.0
Revision Date: 2021-02-23
Group Prepared By: Generic Audio Working Group
Abstract:
This specification describes the service that exposes a control interface and the status of a microphone mute control.
Revision History
|
Revision Number |
Date |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
v1.0 |
2021-02-23 |
Adopted by the Bluetooth SIG Board of Directors. |
Contributors
|
Name |
Company |
|---|---|
|
Michael Rougeux |
Bose Corporation |
|
Siegfried Lehmann |
Apple, Inc. |
|
Tim Reilly |
Bose Corporation |
|
Robin Heydon |
Qualcomm, Inc. |
|
Asbjørn Sæbø |
Nordic Semiconductor ASA |
|
Georg Dickmann |
Sonova AG |
|
Bjarne Klemmensen |
Oticon A/S |
|
HJ Lee |
LG Electronics Inc. |
|
Marcel Holtmann |
Intel Corporation |
|
Masahiko Seki |
Sony Corporation |
|
Søren Møllskov Larsen |
Widex A/S |
|
Daniel Sisolak |
Bose Corporation |
|
Oren Haggai |
Intel Corporation |
|
Frank Yerrace |
Microsoft Corporation |
Use of this specification is your acknowledgement that you agree to and will comply with the following notices and disclaimers. You are advised to seek appropriate legal, engineering, and other professional advice regarding the use, interpretation, and effect of this specification.
Use of Bluetooth specifications by members of Bluetooth SIG is governed by the membership and other related agreements between Bluetooth SIG and its members, including those agreements posted on Bluetooth SIG’s website located at www.bluetooth.com. Any use of this specification by a member that is not in compliance with the applicable membership and other related agreements is prohibited and, among other things, may result in (i) termination of the applicable agreements and (ii) liability for infringement of the intellectual property rights of Bluetooth SIG and its members. This specification may provide options, because, for example, some products do not implement every portion of the specification. Each option identified in the specification is intended to be within the bounds of the Scope as defined in the Bluetooth Patent/Copyright License Agreement (“PCLA”). Also, the identification of options for implementing a portion of the specification is intended to provide design flexibility without establishing, for purposes of the PCLA, that any of these options is a “technically reasonable non-infringing alternative.”
Use of this specification by anyone who is not a member of Bluetooth SIG is prohibited and is an infringement of the intellectual property rights of Bluetooth SIG and its members. The furnishing of this specification does not grant any license to any intellectual property of Bluetooth SIG or its members. THIS SPECIFICATION IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND BLUETOOTH SIG, ITS MEMBERS AND THEIR AFFILIATES MAKE NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES AND DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR THAT THE CONTENT OF THIS SPECIFICATION IS FREE OF ERRORS. For the avoidance of doubt, Bluetooth SIG has not made any search or investigation as to third parties that may claim rights in or to any specifications or any intellectual property that may be required to implement any specifications and it disclaims any obligation or duty to do so.
TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, BLUETOOTH SIG, ITS MEMBERS AND THEIR AFFILIATES DISCLAIM ALL LIABILITY ARISING OUT OF OR RELATING TO USE OF THIS SPECIFICATION AND ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS SPECIFICATION, INCLUDING LOST REVENUE, PROFITS, DATA OR PROGRAMS, OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, HOWEVER CAUSED AND REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY, AND EVEN IF BLUETOOTH SIG, ITS MEMBERS OR THEIR AFFILIATES HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF THE DAMAGES.
Products equipped with Bluetooth wireless technology ("Bluetooth Products") and their combination, operation, use, implementation, and distribution may be subject to regulatory controls under the laws and regulations of numerous countries that regulate products that use wireless non-licensed spectrum. Examples include airline regulations, telecommunications regulations, technology transfer controls, and health and safety regulations. You are solely responsible for complying with all applicable laws and regulations and for obtaining any and all required authorizations, permits, or licenses in connection with your use of this specification and development, manufacture, and distribution of Bluetooth Products. Nothing in this specification provides any information or assistance in connection with complying with applicable laws or regulations or obtaining required authorizations, permits, or licenses.
Bluetooth SIG is not required to adopt any specification or portion thereof. If this specification is not the final version adopted by Bluetooth SIG’s Board of Directors, it may not be adopted. Any specification adopted by Bluetooth SIG’s Board of Directors may be withdrawn, replaced, or modified at any time. Bluetooth SIG reserves the right to change or alter final specifications in accordance with its membership and operating agreements.
Copyright © 2019–2021. All copyrights in the Bluetooth Specifications themselves are owned by Apple Inc., Ericsson AB, Intel Corporation, Lenovo (Singapore) Pte. Ltd., Microsoft Corporation, Nokia Corporation, and Toshiba Corporation. The Bluetooth word mark and logos are owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. Other third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
1. Introduction
This service enables a device to expose the mute control and state of one or more microphones.
1.1. Conformance
If conformance to this specification is claimed, all capabilities indicated as mandatory for this specification shall be supported in the specified manner (process-mandatory). This also applies for all optional and conditional capabilities for which support is indicated.
1.2. Service dependencies
This service depends on the Audio Input Control Service (AICS) [3], if AICS is included by this service.
1.3. Bluetooth Core Specification release compatibility
This specification is compatible with any version of the Bluetooth Core Specification [1] that includes the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT).
1.4. GATT sub-procedure requirements
Requirements in this section represent a minimum set of server requirements. Other GATT sub‑procedures may be used if supported by both the client and server.
Requirements in this section are defined as “Mandatory” (M), “Optional” (O), “Excluded” (X), and “Conditional” (C.n). Conditional statements (C.n) are listed directly below the table in which they appear.
Table 1.1 summarizes additional GATT sub-procedure requirements beyond those required by all GATT servers over Unenhanced Attribute Protocol (ATT) bearers.
|
GATT Sub-Procedure |
Requirements |
|---|---|
|
Write Characteristic Values |
M |
|
Notifications |
M |
|
Read Characteristic Descriptors |
M |
|
Write Characteristic Descriptors |
M |
1.5. Transport dependencies
This service uses GATT and therefore has no additional transport dependencies.
Notifications with GATT are considered unreliable when used with an Unenhanced ATT bearer.
An Enhanced ATT bearer can be used for reliability of Notifications and can be specified by a higher-layer profile.
1.6. Application error codes
This service defines the Application error codes shown in Table 1.2.
|
Name |
Error Code |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Mute Disabled |
0x80 |
Mute/unmute commands are disabled. |
1.7. Byte transmission order
All characteristics used with this service shall be transmitted with the least significant octet (LSO) first (i.e., little endian). The LSO is identified in the characteristic definitions in the Bluetooth SIG Assigned Numbers [4].
1.8. Language
1.8.1. Language conventions
The Bluetooth SIG has established the following conventions for use of the words shall, must, will, should, may, can, is, and note in the development of specifications:
|
shall |
is required to – used to define requirements. |
|
must |
is used to express: a natural consequence of a previously stated mandatory requirement. OR an indisputable statement of fact (one that is always true regardless of the circumstances). |
|
will |
it is true that – only used in statements of fact. |
|
should |
is recommended that – used to indicate that among several possibilities one is recommended as particularly suitable, but not required. |
|
may |
is permitted to – used to allow options. |
|
can |
is able to – used to relate statements in a causal manner. |
|
is |
is defined as – used to further explain elements that are previously required or allowed. |
|
note |
Used to indicate text that is included for informational purposes only and is not required in order to implement the specification. Each note is clearly designated as a “Note” and set off in a separate paragraph. |
For clarity of the definition of those terms, see Core Specification Volume 1, Part E, Section 1.
1.8.2. Reserved for Future Use
Where a field in a packet, Protocol Data Unit (PDU), or other data structure is described as "Reserved for Future Use" (irrespective of whether in uppercase or lowercase), the device creating the structure shall set its value to zero unless otherwise specified. Any device receiving or interpreting the structure shall ignore that field; in particular, it shall not reject the structure because of the value of the field.
Where a field, parameter, or other variable object can take a range of values, and some values are described as "Reserved for Future Use," a device sending the object shall not set the object to those values. A device receiving an object with such a value should reject it, and any data structure containing it, as being erroneous; however, this does not apply in a context where the object is described as being ignored or it is specified to ignore unrecognized values.
When a field value is a bit field, unassigned bits can be marked as Reserved for Future Use and shall be set to 0. Implementations that receive a message that contains a Reserved for Future Use bit that is set to 1 shall process the message as if that bit was set to 0, except where specified otherwise.
The acronym RFU is equivalent to Reserved for Future Use.
1.8.3. Prohibited
When a field value is an enumeration, unassigned values can be marked as “Prohibited.” These values shall never be used by an implementation, and any message received that includes a Prohibited value shall be ignored and shall not be processed and shall not be responded to.
Where a field, parameter, or other variable object can take a range of values, and some values are described as “Prohibited,” devices shall not set the object to any of those Prohibited values. A device receiving an object with such a value should reject it, and any data structure containing it, as being erroneous.
“Prohibited” is never abbreviated.
1.8.4. Terminology
Table 1.3 defines terms that are needed to understand features used in this service.
|
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
gain |
The amplification or attenuation of a signal. |
|
microphone |
A single or group of audio transducers that converts sound to an electrical signal. |
|
Unenhanced ATT bearer |
An ATT bearer not using the Enhanced Credit Based Flow Control Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) channel mode introduced in Volume 3, Part A, Section 10.2 in the Bluetooth Core Specification [2]. |
|
Enhanced ATT bearer |
An ATT bearer using the Enhanced Credit Based Flow Control L2CAP channel mode introduced in Volume 3, Part A, Section 10.2 in [2]. |
2. Service
2.1. Declaration
There shall be no more than one instance of the Microphone Control Service (MICS) on a device. MICS is declared on devices that can control the mute state of a microphone’s audio.
The Attribute Type service declaration shall be set to the «Primary Service» or «Secondary Service» universally unique identifier (UUID), and the Attribute Value service declaration shall be set to the «Microphone Service» as defined in [4].
2.2. Included services
This service may include zero or more instances of AICS [3].
2.2.1. Topology
This service provides global, device-wide, mute control. When included, AICS provides per-input mute and gain control.
2.2.1.1. Microphone Control Service only
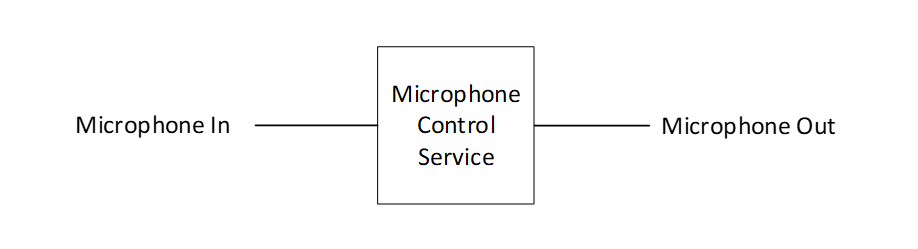
An instance of MICS with no included instances of AICS provides the simplest topology that allows control over the mute state. Devices that do not expose gain control should use the topology shown in Figure 2.1.
2.2.1.2. Microphone Control Service with single Audio Input Control Service
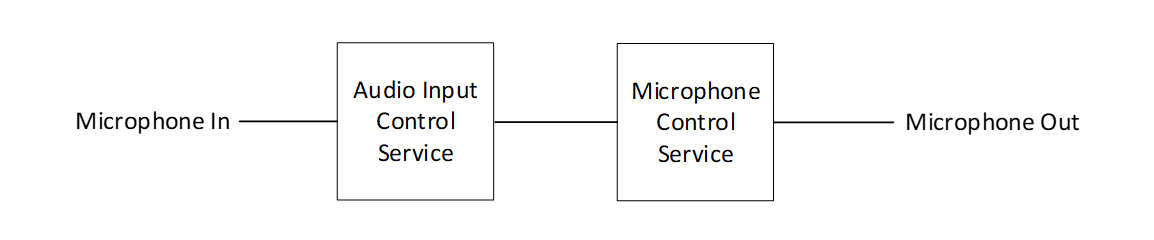
An instance of MICS with one included instance of AICS allows control over device-wide mute and one single-input gain and mute. Devices that expose a single gain control should use the topology shown in Figure 2.2.
2.2.1.3. Microphone Control Service with multiple Audio Input Control Services
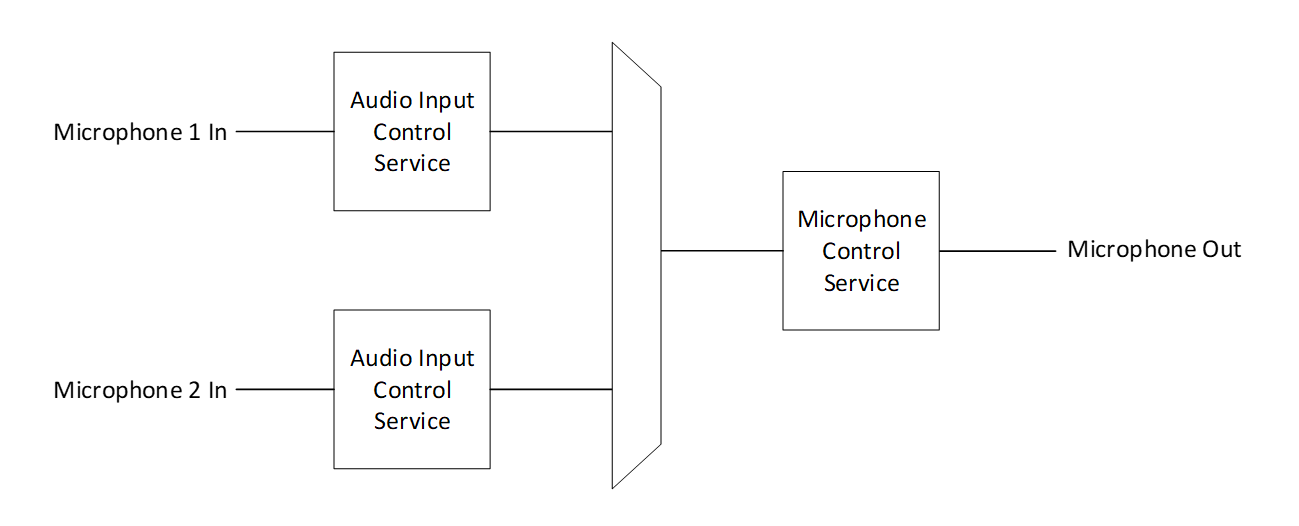
An instance of MICS with multiple included instances of AICS allows control over device-wide mute and the per-input gain and mute of multiple microphones. Devices with multiple individually controllable microphones should use the topology shown in Figure 2.3.
3. Service characteristics
This section defines the characteristic and descriptor requirements.
Requirements in this section are defined as “Mandatory” (M), “Optional” (O), “Excluded” (X), and “Conditional” (C.n). Conditional statements (C.n) are listed directly below the table in which they appear.
|
Characteristic Name |
Requirement |
Mandatory Properties |
Optional Properties |
Security Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Mute |
M |
Read, Write, Notify |
– |
Encryption Required |
3.1. Mute
The Mute characteristic shall be set to a value that reflects the current mute state of the audio to which this service applies. Table 3.2 describes the Mute characteristic values.
|
Description |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Not Muted |
0x00 |
|
Muted |
0x01 |
|
Disabled |
0x02 |
|
RFU |
0x03–0xFF |
The Mute characteristic value represents the server’s audio state, where a value of Not Muted represents unmuted audio, a value of Muted represents muted audio, and a value of Disabled represents that mute commands are disabled (for example, via a local privacy switch or other means) and the microphone is muted.
3.1.1. Mute behavior
The Mute characteristic value may be read or written. When the Mute characteristic is configured for notification via the Client Characteristic Configuration descriptor, this value shall be notified when changed. When the Mute characteristic value is changed by the server or a client, then this value shall be notified to all clients that have enabled the Client Characteristic Configuration descriptor for notifications.
If the client writes a value of Disabled or RFU to the Mute characteristic, the server shall return an ATT Error Response with the ATT error code Value Not Allowed (0x13) as defined in [1].
If the client writes to the Mute characteristic when the Mute characteristic value is Disabled, the server shall return an ATT Error Response with the error code Mute Disabled (0x80) as defined in Table 1.2. Only a local change on the server may transition the value from Disabled to another value.
4. SDP interoperability
If MICS is exposed over Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate (BR/EDR), then the server shall have the Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) record defined in Table 4.1.
Requirements in this section are defined as “Mandatory” (M), “Optional” (O), “Excluded” (X), and “Conditional” (C.n). Conditional statements (C.n) are listed directly below the table in which they appear.
|
Item |
Definition |
Type |
Value |
Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Service Class ID List |
– |
– |
– |
M |
|
Service Class #0 |
– |
UUID |
«Microphone Control Service» |
M |
|
Protocol Descriptor List |
– |
Data Element Sequence |
– |
M |
|
Protocol #0 |
– |
UUID |
«L2CAP» |
M |
|
Parameter #0 for Protocol #0 |
Protocol/Service Multiplexer (PSM) |
Uint16 |
PSM = ATT |
M |
|
Protocol #1 |
– |
UUID |
«ATT» |
M |
|
Additional Protocol Descriptor List |
– |
Data Element Sequence |
– |
C.1 |
|
Protocol Descriptor List |
– |
Data Element Sequence |
– |
C.1 |
|
Protocol #0 |
– |
UUID |
«L2CAP» |
C.1 |
|
Parameter #0 for Protocol #0 |
PSM |
Uint16 |
PSM = EATT |
C.1 |
|
Protocol #1 |
– |
UUID |
«ATT» |
C.1 |
|
BrowseGroupList |
– |
– |
PublicBrowseRoot Other browse UUIDs may also be included in the list. |
M |
C.1: Mandatory if Enhanced Attribute Protocol (EATT), introduced in Volume 3, Part F, Section 3.2.11 in [2], is supported, otherwise Excluded.
5. Acronyms and abbreviations
|
Acronym/Abbreviation |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
AICS |
Audio Input Control Service |
|
ATT |
Attribute Protocol |
|
BR/EDR |
Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate |
|
EATT |
Enhanced Attribute Protocol |
|
GATT |
Generic Attribute Profile |
|
L2CAP |
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol |
|
LSO |
least significant octet |
|
MICS |
Microphone Control Service |
|
PDU |
Protocol Data Unit |
|
PSM |
Protocol/Service Multiplexer |
|
RFU |
Reserved for Future Use |
|
SDP |
Service Discovery Protocol |
|
UUID |
universally unique identifier |
6. References
[1] Bluetooth Core Specification, Version 4.0 or later
[2] Bluetooth Core Specification, Version 5.2
[3] Audio Input Control Service Specification, Version 1.0
[4] Bluetooth SIG Assigned Numbers, https://www.bluetooth.com/specifications/assigned-numbers
